The MRZ number on a passport is a string of characters that appears at the bottom of the personal data page, containing letters, numbers, and symbols arranged in three lines. It is used for identity verification and is one of the core security features in passports, ID cards, visas, and many other identity documents.
The MRZ follows strict rules that determine how passport information is shown. The machine-readable zone (MRZ) is a crucial aspect of identity verification that encodes essential information about the passport holder. The MRZ is a string of characters that appears at the bottom of the passport’s personal data page, containing letters, numbers, and symbols arranged in three lines.
It is used for identity verification and is one of the core security features in passports, ID cards, visas, and many other identity documents. The MRZ follows strict rules that determine how passport information is shown, making it a reliable tool for identity verification. This article will explore the MRZ code and its role in identity verification.
Credit: www.idenfy.com
What Is Passport Mrz?
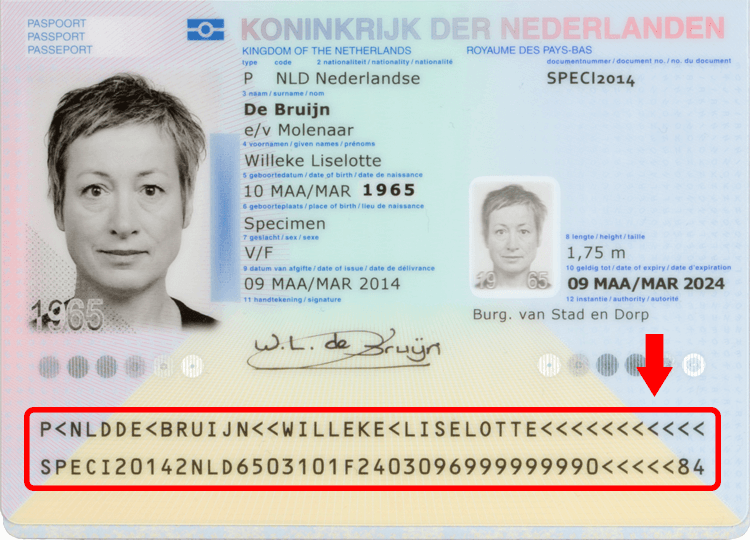
Passport MRZ, or Machine Readable Zone, is a particular area in an identity document, specifically a passport, that encloses the document holder’s essential information. This includes the passport holder’s name, nationality, date of birth, and passport number. The MRZ is typically located at the bottom of the passport’s personal data page and contains a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols arranged in three lines.

Credit: www.mindee.com
Components Of Passport Mrz
Passport MRZ (Machine-Readable Zone) is a crucial component of modern passports, providing a standardized format for the alphanumeric data found on the identification page. This two-line code is essential for automated data entry and is commonly used for identity verification and border control purposes. Understanding the components of Passport MRZ is vital for anyone dealing with travel documentation and identity management.
Two Lines Of Text
The two lines of text in a Passport MRZ contain essential information such as the document type, issuing country or organization, the name of the document holder, document number, nationality, birth date, and expiration date. This information is crucial for automatic identification and verification processes at immigration checkpoints, airports, and other official points of entry. The format of the two lines is standardized to facilitate machine readability and data extraction, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
- Document Type
- Issuing Country or Organization
- Name of the Document Holder
- Document Number
- Nationality
- Birth Date
- Expiration Date
Machine-readable Zone (mrz)
The Machine-Readable Zone (MRZ) is a specially designated area at the bottom of the identification page of a passport, containing the two lines of text. This zone is designed to be easily readable by machine scanners and optical character recognition (OCR) software. The MRZ utilizes a specific format for organizing and presenting the alphanumeric data, including check digits and special characters, to ensure accuracy and prevent unauthorized alterations. It serves as a reliable means of extracting and verifying passport information, contributing to streamlined border control procedures and enhanced security measures.
Why Is Passport Mrz Important?
Passport MRZ, also known as the Machine Readable Zone, is an essential component of a passport that plays a crucial role in ensuring security and ease of processing. The MRZ is a line of characters located at the bottom of the passport, containing a combination of digits, letters, and chevrons. But why is Passport MRZ important? Let’s delve deeper into its significance.
Security Features
One of the primary reasons why Passport MRZ is important is its robust security features. The MRZ contains encoded information that is difficult to alter or counterfeit, making it an effective tool in preventing identity theft and passport fraud. The data within the MRZ includes the passport holder’s personal details such as name, date of birth, and passport number. By utilizing advanced encryption techniques, the MRZ ensures that only authorized individuals can access and decipher this sensitive information.
Furthermore, the MRZ incorporates various security elements such as check digits and data consistency checks. These features enable automated systems and border control officers to quickly verify the authenticity and integrity of the passport, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. The MRZ acts as a secure gateway, allowing seamless travel while maintaining the highest level of security.
The table below highlights some of the key security features of Passport MRZ:
| Security Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoded Information | The MRZ contains encrypted data that is difficult to forge or tamper with. |
| Check Digits | Check digits enable quick verification of the MRZ data’s accuracy and integrity. |
| Data Consistency Checks | The MRZ undergoes consistency checks to ensure that the information is valid and matches the passport holder’s details. |
Ease Of Processing
In addition to its security features, Passport MRZ significantly contributes to the ease and efficiency of passport processing. The machine-readable format of the MRZ allows automated systems to quickly read and extract the encoded information, reducing manual data entry and potential errors. This streamlined process enhances the speed of passport checks, enabling smoother travel experiences for individuals.
The MRZ’s machine-readable format also facilitates seamless integration with various travel and identity verification systems worldwide. This compatibility ensures interoperability across different countries and enables efficient data sharing, enhancing border control operations and international security cooperation.
Moreover, the MRZ simplifies the process of retrieving passport holder information for immigration officers and other authorized personnel. With a quick scan or input of the MRZ, relevant details can be accessed, saving time and improving overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, Passport MRZ is a vital component of modern passports, providing robust security features and enhancing the ease of processing. Its encoded information and advanced encryption techniques protect against identity theft and passport fraud, while its machine-readable format enables seamless and efficient passport checks. As technology continues to advance, the importance of Passport MRZ in ensuring secure and hassle-free travel experiences will only grow.
How To Read Passport Mrz
Passport MRZ, or Machine Readable Zone, is an essential component of passports that allows for easy and accurate identification of individuals. Understanding how to read the Passport MRZ is crucial for various purposes, including border control, identity verification, and travel documentation. In this section, we will explore two methods for reading Passport MRZ: Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Manual Entry.
Optical Character Recognition (ocr)
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that enables the automatic extraction of text from images. When it comes to reading Passport MRZ, OCR plays a vital role in quickly and accurately capturing the necessary information. Here’s how OCR works in the context of Passport MRZ:
- Passport MRZ consists of two lines of text, which are typically printed at the bottom of the passport’s personal data page.
- OCR software utilizes advanced algorithms to analyze the image of the Passport MRZ and extract the relevant characters.
- The extracted characters are then converted into digital text, which can be further processed and utilized for various applications.
OCR technology has significantly improved over the years, allowing for high accuracy in reading Passport MRZ. It eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing the possibility of human errors. Moreover, OCR enables fast and efficient processing of large volumes of passports, making it an invaluable tool for immigration authorities and other organizations that deal with passport data.
Manual Entry
In certain situations, manual entry of Passport MRZ may be required. This method involves manually inputting the characters from the MRZ into a computer system or application. Here’s what you need to know about manual entry of Passport MRZ:
- The MRZ number is the long number at the bottom of the passport that contains a combination of digits, letters, and chevrons.
- To manually enter the MRZ, you need to accurately input each character into the designated fields, ensuring no mistakes are made.
- While manual entry may be necessary in some cases, it is important to exercise caution and double-check the entered data to avoid any inaccuracies.
Manual entry of Passport MRZ can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially when dealing with a large number of passports. Therefore, it is recommended to utilize OCR technology whenever possible to streamline the process and ensure data accuracy.
What Information Is Contained In Passport Mrz?
Passport MRZ, short for Machine Readable Zone, is a unique code at the bottom of every passport page. It contains all the necessary information about the passport holder and the passport itself. Knowing what information is included in the MRZ is essential for travelers, immigration officers, and border control agents. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the information contained in Passport MRZ and why it’s important.
Personal Information
The personal information of the passport holder is the first section of the MRZ. It contains the following details:
- Surname
- Given name(s)
- Nationality
- Date of birth
- Gender
- Passport expiration date
All of this information is important for verifying the identity of the passport holder and ensuring that the passport is valid. The passport holder’s name, nationality, and date of birth are crucial pieces of information for immigration officers and border control agents to confirm that the person holding the passport is who they claim to be. Gender is included in the MRZ to avoid any confusion that may arise from differences in naming conventions across different cultures. Finally, the passport expiration date is necessary to ensure that the passport is still valid and has not expired.
Passport Information
The second section of the MRZ contains information about the passport itself. This section includes:
- Passport number
- Country code
- Passport issue date
- Passport type
- Check digit
The passport number is a unique identifier that distinguishes one passport from another. The country code is a three-letter code that indicates the country that issued the passport. The passport issue date is the date on which the passport was issued. The passport type indicates the type of passport issued, such as a regular passport or a diplomatic passport. Finally, the check digit is a single digit used to verify that all the information in the MRZ has been correctly read and interpreted.
In conclusion, the MRZ is an essential part of every passport, containing all the necessary information about the passport holder and the passport itself. Personal information and passport information are the two main sections of the MRZ, and each plays a crucial role in verifying the identity of the passport holder and ensuring that the passport is valid. Understanding what information is contained in Passport MRZ is essential for anyone who travels internationally or works in immigration or border control.
Limitations Of Passport Mrz
Passport MRZ, also known as the Machine-Readable Zone, is a vital component of modern passports. It is a strip of characters at the bottom of the passport that contains the holder’s personal information, including their name, date of birth, and passport number. While the MRZ has been instrumental in speeding up the process of passport control, it has some limitations that are worth noting.
Potential For Fraud
One of the primary concerns with the MRZ is its potential for fraud. Since the MRZ contains critical personal information, it can be a target for identity thieves and fraudsters. They can use the MRZ to create fake passports or to steal someone’s identity. Moreover, MRZs are susceptible to tampering and alteration, which makes it difficult for authorities to detect fraud.
Here are some examples of how fraudsters can use the MRZ to commit fraud:
- They can create fake passports using someone else’s MRZ.
- They can change the MRZ information to match their own details.
- They can use the MRZ to steal someone’s identity, making it easier to commit other types of fraud.
Therefore, while the MRZ has made passport control more efficient, it has also introduced new security risks that authorities must address.
Errors In Reading
Another limitation of the MRZ is that it is prone to errors in reading. MRZ readers rely on the accuracy of the printed characters to read the information correctly. However, if there are any smudges, scratches, or other defects in the MRZ, the reader may have difficulty reading the information. Moreover, if the MRZ is damaged, it may be impossible to read the information at all.
Here are some examples of how errors in reading can occur:
- If the MRZ is damaged, it may be impossible to read the information.
- If the MRZ is smudged or scratched, the reader may misinterpret the information.
- If the MRZ is printed incorrectly, the reader may not be able to read the information.
Therefore, while the MRZ has been a significant improvement in passport control, it is not foolproof. Errors in reading can occur, which can lead to delays and inconvenience for travelers.
Future Of Passport Mrz
The future of Passport MRZ is an exciting one, as digitalization and alternative technologies continue to shape the way we travel and authenticate our identities. In this blog post, we will explore the impact of digitalization and alternative technologies on Passport MRZ and how they are revolutionizing the way we use passports.
Digitalization
Digitalization has brought about significant advancements in the field of passport technology. Traditional passports with MRZ codes are now being replaced by e-passports, which incorporate digital features and biometric data. This shift towards digitalization offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Security: E-passports use advanced encryption and security measures to protect personal information, making it more difficult for fraudsters to tamper with or forge passports.
- Efficient Travel: Digital passports allow for faster and more streamlined travel experiences, as they can be quickly scanned and verified at immigration checkpoints.
- Convenience: With digital passports, travelers no longer need to carry physical documents, reducing the risk of loss or theft. Passports can be stored securely on smartphones or other digital devices.
Overall, digitalization is revolutionizing the way we interact with passports, making travel more secure, efficient, and convenient.
Alternative Technologies
In addition to digitalization, alternative technologies are also being explored to enhance passport MRZ systems. These technologies aim to further improve security and streamline the passport authentication process. Some of the alternative technologies being considered include:
- Biometric Authentication: Biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, can be integrated into passport systems to provide an additional layer of security. This technology ensures that the person presenting the passport is the genuine owner.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize passport MRZ systems by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof platform for storing and verifying passport data. This technology can enhance security and prevent identity fraud.
- NFC (Near Field Communication): NFC technology enables secure communication between devices in close proximity. By incorporating NFC into passports, authorities can quickly authenticate and verify passport data using compatible devices.
These alternative technologies offer promising solutions to enhance passport MRZ systems and improve the overall travel experience. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in the field of passport authentication.

Credit: egov.ice.gov
Frequently Asked Questions
Where Is The Mrz Number On Passport?
The MRZ number on a passport is located at the bottom of the passport. It is a long number that contains a combination of digits, letters, and chevrons. The MRZ code is a string of characters arranged in three lines on the bottom of the personal data page of the passport.
How Do I Find My Mrz Code?
To find your MRZ code, look at the bottom of your passport’s personal data page. The MRZ is a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols arranged in three lines.
What Is The Mrz Column Of The Passport?
The MRZ column is the long string of characters at the bottom of the passport containing letters, digits, and chevrons. It’s used for machine-readable data processing.
What Is The Check Digit In Mrz On Passport?
The check digit in MRZ on a passport is a single digit calculated from other digits in the series. It allows readers to verify the data in the MRZ for accuracy.
What Is The Mrz Number On A Passport?
The MRZ number is a long string of characters containing digits, letters, and chevrons located at the bottom of the passport.
How Do I Find My Mrz Code?
The MRZ code is located at the bottom of the personal data page of a passport. It consists of letters, numbers, and symbols arranged in three lines.
Conclusion
The Machine-Readable Zone (MRZ) on a passport plays a crucial role in identity verification and protection. It is a unique combination of letters, numbers, and symbols arranged in three lines at the bottom of the personal data page. The MRZ code allows for easy processing by machines and helps prevent identity theft.
By understanding the significance of the MRZ, individuals can ensure the security of their passports and personal information.

